This is a recording of a recent live teleclass I did with thousands of kids from all over the world. I’ve included it here so you can participate and learn, too! (Click here if you’re looking for the more recent version that also includes Chemical Engineering.)
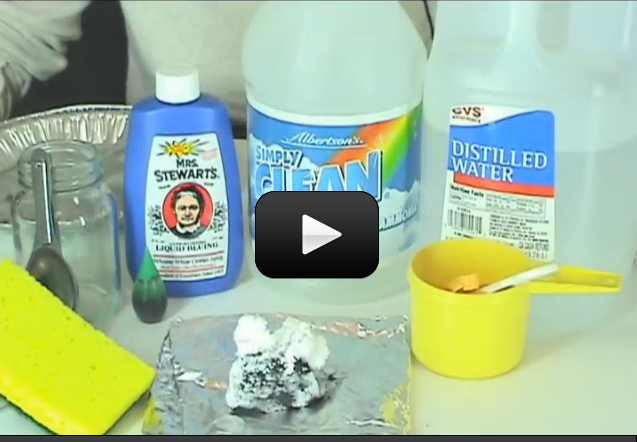
When you think of slime, do you imagine slugs, snails, and puppy kisses? Or does the science fiction film The Blob come to mind? Any way you picture it, slime is definitely slippery, slithery, and just plain icky — and a perfect forum for learning real science. But which ingredients work in making a truly slimy concoction, and why do they work? Let’s take a closer look…
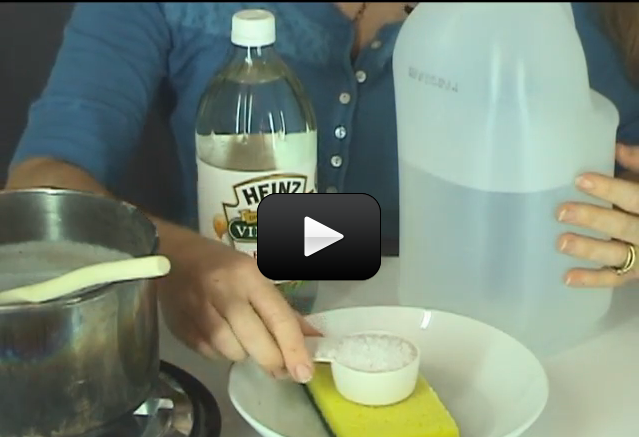
Materials:
- Sodium tetraborate (also called “Borax” – it’s a laundry whitener) – about 2 tablespoons
- Clear glue or white glue (clear works better if you can find it) – about 1/2 cup
- Yellow highlighter
- Pliers or sharp razor (with adult help). (PREPARE: Use this to get the end off your highlighter before class starts so you can extract the ink-soaked felt inside. Leave the felt inside highlighter with the end loosely on (so it doesn’t dry out))
- Resuable Instant Hand Warmer that contains sodium acetate (Brand Name: EZ Hand Warmer) – you’ll need two of these
- Scissors
- Glass half full of COLD water (PREPARE: put this in the fridge overnight)
- Mixing bowl full of ice (PREPARE: leave in freezer)
- Salt
- Disposable aluminum pie place or foil-wrapped paper plate
- Disposable cups for solutions (4-6)
- Popsicle sticks for mixing (4-6)
- Rubber gloves for your hands
- Optional: If you want to see your experiments glow in the dark, you’ll need a fluorescent UV black light (about $10 from the pet store – look in cleaning supplies under “Urine-Off” for a fluorescent UV light). UV flashlights and UV LEDs will not work.
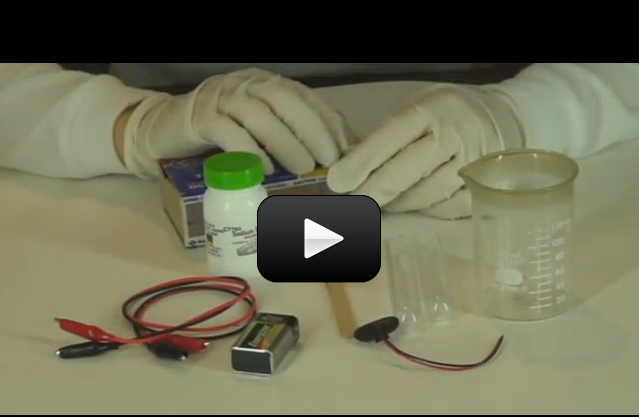
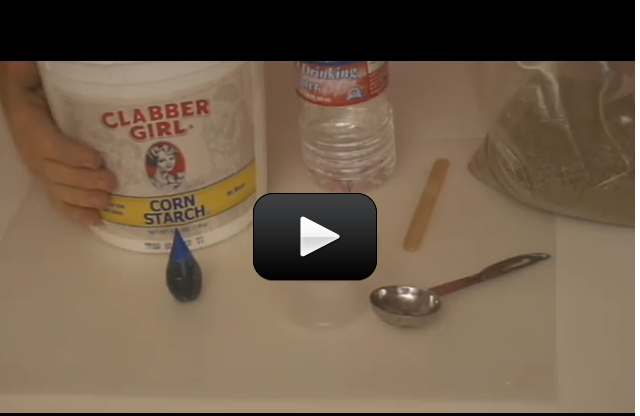






 When you warm up leftovers, have you ever wondered why the microwave heats the food and not the plate? (Well, some plates, anyway.) It has to do with the way microwaves work.
When you warm up leftovers, have you ever wondered why the microwave heats the food and not the plate? (Well, some plates, anyway.) It has to do with the way microwaves work.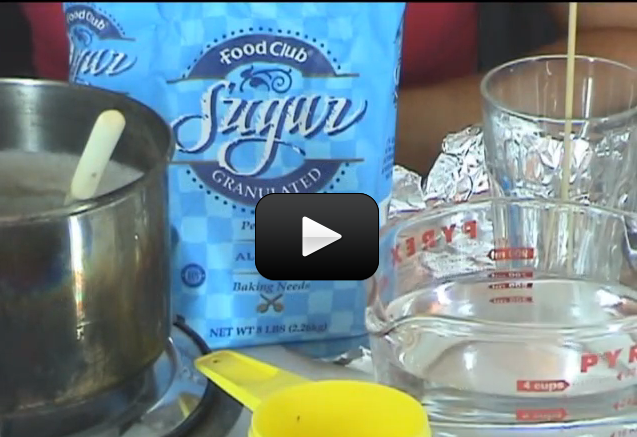

 The atoms in a solid, as we mentioned before, are usually held close to one another and tightly together. Imagine a bunch of folks all stuck to one another with glue. Each person can wiggle and jiggle but they can’t really move anywhere.
The atoms in a solid, as we mentioned before, are usually held close to one another and tightly together. Imagine a bunch of folks all stuck to one another with glue. Each person can wiggle and jiggle but they can’t really move anywhere.
 Can we really make crystals out of soap? You bet! These crystals grow really fast, provided your solution is properly saturated. In only 12 hours, you should have sizable crystals sprouting up.
Can we really make crystals out of soap? You bet! These crystals grow really fast, provided your solution is properly saturated. In only 12 hours, you should have sizable crystals sprouting up.

 Density is basically how tightly packed atoms are. Mathematically, density is mass/volume. In other words, it is how heavy something is, divided by how much space it takes up. If you think about atoms as marbles (which we know they’re not from the last lessons but it’s a useful model), then something is more dense if its marbles are jammed close together.
Density is basically how tightly packed atoms are. Mathematically, density is mass/volume. In other words, it is how heavy something is, divided by how much space it takes up. If you think about atoms as marbles (which we know they’re not from the last lessons but it’s a useful model), then something is more dense if its marbles are jammed close together.

 This is a simple experiment that really shows the relationship of mass, volume, and density. You don't need anything fancy, just a piece of bread. If you do have a scale that can measure small masses (like a kitchen scale), bring it out, but it is not essential.
This is a simple experiment that really shows the relationship of mass, volume, and density. You don't need anything fancy, just a piece of bread. If you do have a scale that can measure small masses (like a kitchen scale), bring it out, but it is not essential.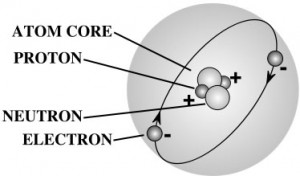
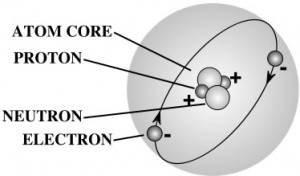 A gram of water (about a thimble of water) contains 1023 atoms. (That’s a ‘1’ with 23 zeros after it.) That means there are 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 atoms in a thimble of water! That’s more atoms than there are drops of water in all the lakes and rivers in the world.
A gram of water (about a thimble of water) contains 1023 atoms. (That’s a ‘1’ with 23 zeros after it.) That means there are 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 atoms in a thimble of water! That’s more atoms than there are drops of water in all the lakes and rivers in the world.




