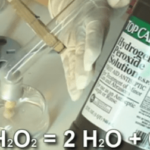Reducing Agent Orange
Today we will investigate the reducing power of orange. |
Potassium Hexacyanoferrate Reagent
Today we will be investigating potassium hexacyanoferrate as a detection agent for metals, specifically iron. |
Introduction: Kit Overview, Tripod Assembly, Alcohol Burner Assembly, Insertion and Removal of Glass Tubing in Rubber Stopper
Welcome! Today we will be discussing tips on setting up your work station, and going over the contents in your chemistry kit. |
Introduction: Household Items Needed and Chemicals to be Ordered
Today we will be gathering items needed that are not provided in the kit. |
Silver Nitrate Reagent Part 1
Today we will learn another separation technique and how to use silver nitrate to detect chloride in a solution. |
Synthesizing Copper Sulfate
Today we will be synthesizing and analyzing copper sulfate. |
Introduction: Solution Preparation
Today we will be diluting and preparing solutions. |
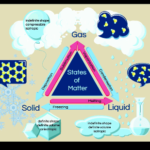
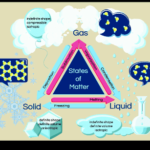
Phases of Water Part 1
Today we will be covering part 1 of the phases of water. |
Phases of Water Part 2
Today we will be covering part 2 of the phases of water, and learning about distillation. |
Water Purification
Today we will be investigating how to purify water. |
Cooling Crystallization
Today we will investigate crystallization through cooling and how it can be used as a separation and purification technique. |
Electrolysis Part 2
Today we will investigate how to split water molecules with electricity in a process known as electrolysis. |
Gases
Today we will investigate air pressure and gases. |
Potassium Permanganate Experiments
Today we will be investigating potassium permanganate. |
Combustion
Today we will be studying combustion. |
Hydrogen from Magnesium and Aluminum
Today we will produce hydrogen gas from magnesium and aluminum. |
Calcium Hydroxide Reagent
Today we will study calcium hydroxide and how it can used as a reagent. |
Silverware Polishing
Today we will learn about polishing silver. |
Potassium Permanganate and Hydrogen Peroxide
Today we will be investigating potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide. |
Catalyst: Potassium Iodide (KI)
Today we will investigate how potassium iodide can be used as a catalyst. |
Activated Charcoal
Today we will be studying activated charcoal. |
Decomposing through Heavy Metals
Today we will be studying how hydrogen peroxide decomposes through heavy metals. |
Iron Sulfide and Sulfur
Today we will be producing hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide gases. |
Baking Soda
Today we will compare sodium carbonate (also known as soda), and sodium bicarbonate (which is known as baking soda). |
Alkaline Earth Metals: Magnesium
Today we will be investing the alkaline earth metal: Magnesium. |
Copper Part 1
Today we will be covering part 1 in our investigation into copper. |
Hydrogen Chloride Part 2
Today we will be continuing our investigation of hydrogen chloride. |
Electrolytes: Conductors or Non-Conductors? Part 2
Today we will be covering part 2 of our investigation of whether electrolytes conduct or don’t conduct electricity. |
Hydrogen Chloride Part 1
Today we will be investigating hydrogen chloride. |
Chlorine Part 1
Today we will cover part 1 of our chlorine investigation. |
Hydrogen Bromide
Today we will be producing and analyzing a solution of hydrogen bromide. |
Electrolytes: Conductors or Non-Conductors? Part 1
Today we will be doing part 1 of our investigation into electrolytes and discovering whether they are conductors or non-conductors. |
Chlorine Part 2
Today we will be caovering part 2 of our investigation into chlorine. |
Iodine
Today we will be investigation iodine. |
Silver Nitrate Reagent Part 2
Today we will be covering part 2 of utilizing silver nitrate as a reagent. |
Starch-Iodine Complex
Today we will be learning about the starch iodine complex |
Redox Reactions of Halogens
Today we will be learning about redox reactions. |
Specters in Chemistry
Today we will witness the appearance and disappearance of a specter in our lab, and learn the chistry behind it. |
Zinc Dust
Today we will be |
Electrolysis of Halogenides
Today we will be |
Delayed Ignition with Potassium Permanganate
Today we will be investigation potassium permanganate and its role as an oxidizer. |
Electrochemical Reactions
Today we will be performing electrochemical analysis of metals. |
Galvanic Cells
Today we will be learning about galvanic cells. |
Litmus with Acids and Bases
Today we will be investigating acids and bases using litmus solutions. |
Copper Salts
Today we will be investigating copper salts. |
Acidic and Basic Salts
Today we will be studying acidic and basic salts. |
Titration
Today we will be investigating titration. |
Desiccants
Today we will be learning about the desiccate calcium chloride. |
Water of Crystallization
Today we will be learning about water of crystallization and the important role it play in the crystalline structure of molecules. |
Sulfur Sulfate
Today we will be investigating sulfur sulfates, more commonly known as thiosulfates. |
Acid Rain
Today we will be investigating acid rain. |
Halogen Reducing Agent
Today we will investigate the reducing effect of sodium thiosulfate. |
Preparation of Iodine Solution
C3000 Experiment: 135 |
Ammonia
Today we will be investigating ammonia. |
Carbon Dioxide
Today we will be setting up a carbon dioxide generator and studying carbon dioxide |
Mineral Water
Today we will be learning about mineral water. |
Carbon Dioxide Fountain & Furnace
Today we will be creating a carbon dioxide fountain and a carbon dioxide furnace. |
Aluminum
Today we will be experimenting with aluminum. |
Flame Test for Chemicals
Today we will learn how to identify certain chemicals by how they burn. |
Zinc
Today we will be working with the transition metal zinc. |
Iron
Today we will be investigating iron |
Copper Part 2
Today we will be covering part 2 in our investigation of copper. |
Sliver
Today we will be investigating silver. |
Polar and Non-Polar Compounds
Today we will be learning about polar and non-polar compounds. |
Hydrocarbons
Today we will investigate hydrocarbons, molecules made up on hydrogen and carbons. |
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Today we will utilize the Bayer test to detect unsaturated fatty acids. |
Hydrogen and Halogens
Today we will be investigating hydrogen and halogens and how halogens can replace hydrogens in molecular compounds. |
Splitting Molecules
Today we will be splitting molecules. |
Acetic Ester
Today we will prepare acidic ester, which is found in glue, and gives off a fruity touch to soft drinks and candies. |
Preparation of Bromine Water
|
From Fat to Soap
Today we will be learning how soap is prepared from fats |
Soap and Hard Water
Today we will investigate the effect of hard water on different types of soaps. |
Soap and Acids
Today we will determine the effect of acid on soaps. |
Breaking Down Starch
Today we will be testing starch’s ability to reduce Fehling solution. |
Starch: Soluble and Insoluble
Today we will be investigating starch in its soluble and insoluble forms. |
Mirror in a Test Tube
Today we will be creating a mirror inside of a test tube. |
Fehling’s Solutions Sugar Test
Today we will be utilizing the Fehling’s test to detect sugars. |
Surfactants
Today we will be learning about surfactants. |
Glucose
Today we will be working with glucose |
Proteins
Today we will begin our investigation in proteins. |
Detecting Proteins in Food
Today we will be utilizing the biuret reaction to detect proteins in various foods. |
Catalase
|
Separating Mixtures
Today we will investigate how mixtures can be separated. |
Basic Chemistry Safety Information
Chemical Data & Safe Handling Information Sheet What do I really need to know first? First of all, the chemicals in this set should be stored out of reach of pets and children. Grab the chemicals right now and stuff them in a safe place where accidents can’t happen. Do this NOW! When you’re done … Continue reading "Basic Chemistry Safety Information" |
Making Litmus Solution and Paper
You can go your whole life without paying any attention to the chemistry behind acids and bases. But you use acids and bases all the time! They are all around you. We identify acids and bases by measuring their pH. Every liquid has a pH. If you pay particular attention to this lab, you will … Continue reading "Making Litmus Solution and Paper" |
Magnesium Battery
Magnesium is one of the most common elements in the Earth’s crust. This alkaline earth metal is silvery white, and soft. As you perform this lab, think about why magnesium is used in emergency flares and fireworks. Farmers use it in fertilizers, pharmacists use it in laxatives and antacids, and engineers mix it with aluminum … Continue reading "Magnesium Battery" |
Making Copper
In this lab, we’re going to investigate the wonders of electrochemistry. Electrochemistry became a new branch of chemistry in 1832, founded by Michael Faraday. Michael Faraday is considered the “father of electrochemistry”. The knowledge gained from his work has filtered down to this lab. YOU will be like Michael Faraday. I imagined he would have … Continue reading "Making Copper" |
Making Chlorine
If we don’t have salt, we die. It’s that simple. The chemical formula for salt is NaCl. Broken down, we have Na (sodium) and Cl (chlorine). Either one of these can be fatal in sufficient quantities. When chemically combined, these two deadly elements become table salt. What once could kill now keeps us alive. Isn’t … Continue reading "Making Chlorine" |
Electrochemistry
Electricity. Chemistry. Nothing in common, have nothing to do with each other. Wrong! Electrochemistry has been a fact since 1774. Once electricity was applied to particular solutions, changes occurred that scientists of the time did not expect. In this lab, we will discover some of the same things that Farraday found over 300 years ago. … Continue reading "Electrochemistry" |
Ammonia Experiments
Ammonia has been used by doctors, farmers, chemists, alchemists, weightlifters, and our families since Roman times. Doctors revive unconscious patients, farmers use it in fertilizer, alchemists tried to use it to make gold, weightlifters sniff it into their lungs to invigorate their respiratory system and clear their heads prior to lifting tremendous loads. At home, … Continue reading "Ammonia Experiments" |
Energy from Sugar
This experiment is for advanced students. Purple and white colors, making the whitewash that Tom Sawyer used, and produce an exothermic chemical reaction…..does it get any better? Limewater is one of the compounds we work with in this experiment. Limewater was used in the old days of America. We’re talking about the 80’s…..the 1880’s. Traveling … Continue reading "Energy from Sugar" |
Getting Air from Water
This experiment is for advanced students. This is a repeat of the experiment: Can Fish Drown? but now we’re going to do this experiment again with your new chemistry glassware. The aquarium looked normal in every way, except for the fish. They were breathing very fast and sinking head first to the bottom of the … Continue reading "Getting Air from Water" |
Working with Cataylsts
This experiment is for advanced students. Don’t put this in your car….yet. Hydrogen generation, capture, and combustion are big deals right now. The next phase of transportation, and a move away from fossil fuels in not found in electric cars. Electric cars are waiting until hydrogen fuel cell vehicles become practical. It can be done … Continue reading "Working with Cataylsts" |
Hydrogen Peroxide
This experiment is for advanced students. In industry, hydrogen peroxide is used in paper making to bleach the pulp before they form it into paper. Biologists, when preparing bones for display, use peroxide to whiten the bones. At home, 3% peroxide combined with ammonium hydroxide is used to give dark-haired people their desired blonde moment. … Continue reading "Hydrogen Peroxide" |
Generating Oxygen
This experiment is for advanced students. This time we’re going to use a lot of equipment… really break out all the chemistry stuff. We’ll need all this stuff to generate oxygen with potassium permanganate (KMNO4). We will work with this toxic chemical and we will be careful…won’t we? |
Detonating Bubbles
This experiment is for advanced students. Zinc (Zn), is a metal and it is found as element #30 on the periodic table. We need a little zinc to keep our bodies balanced, but too much is very dangerous. Zinc is just like the common, everyday substance that we all know as di-hydrogen monoxide (which is … Continue reading "Detonating Bubbles" |
Desalination
This experiment is for advanced students. Lewis and Clark did this same experiment when they reached the Oregon coast in 1805. Men from the expedition traveled fifteen miles south of the fort they had built at the mouth of the Columbia River to where Seaside, Oregon now thrives. In 1805, however, it was just men … Continue reading "Desalination" |
Carbon Dioxide
This experiment is for advanced students. This lab builds on concepts from the previous carbon dioxide lab. Limewater….carbon dioxide…indicators. We don’t know too much about these things. Sure, we know a little. Carbon dioxide is exhaled by us and plants need it to grow. Burning fossil fuels produces carbon dioxide. Indicators…something we observe that confirms … Continue reading "Carbon Dioxide" |
Zinc Dust
This experiment is for advanced students. Who gets to burn something today? YOU get to burn something today! You will be working with Zinc (Zn). Other labs in this kit allow us to burn metal, but there is a bit of a twist this time. We will be burning a powder. Why a powder instead … Continue reading "Zinc Dust" |
Burning Sulfur
This experiment is for advanced students. Brimstone is another name for sulfur, and if you’ve ever smelled it burn…..whoa….I’m telling you ….you will see for yourself in this lab. It is quite a smell, for sure. Sulfur is element #6 on the periodic table. Sulfur is used in fertilizer, black powder, matches, and insecticides. In … Continue reading "Burning Sulfur" |
Acids and Bases
This experiment is for advanced students. ACID!!! The word causes fear to creep in and get our attention. BASIC!!! The word causes nothing to stir in most of us. The truth is, a strong acid (pH 0-1) is dangerous, but a strong basic (pH 13-14) is just as dangerous. In this lab, we will get … Continue reading "Acids and Bases" |
Making Sodium Hydroxide
This experiment is for advanced students. Ever use soap? Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is the main component in lye soap. NaOH is mixed with some type of fat (vegetable, pig, cow, etc). Scent can be added for the ‘pretty’ factor and pumice or sand can be added for the manly “You’re coming off my hands and … Continue reading "Making Sodium Hydroxide" |
Potassium Permanganate
This experiment is for advanced students. Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) in water turns an intense, deep, purple. It is important in the film industry for aging props and clothing to make them look much older than they are. Also, artists use it in bone carving. People who carve antlers and bone use KMnO4 to darken the … Continue reading "Potassium Permanganate" |
Potassium Hexacynoferrate (Reagant)
This experiment is for advanced students. How do you know if your brother is stealing your candy? Unwrap a wrapped hard candy that he likes a lot. Roll the candy around in the powdered food dye that matches the candy. (Push the powder into the candy so it “disappears”.) Re-wrap the candy. Set the candy … Continue reading "Potassium Hexacynoferrate (Reagant)" |
Iodine
This experiment is for advanced students. In gas form, element #59 is deadly. However, when iodine is in liquid form, it helps heal cuts and scrapes. The iodine molecule occurs in pairs, not as a single atom (many halogens do this, and it's called a diatomic molecule). It's hard to find iodine in nature, though … Continue reading "Iodine" |
How to Get Hydrogen from Zinc
This experiment is for advanced students. Zinc and Hydrogen are important elements for all of us. Zinc (Zn) metal is element #30 on the periodic table. Lack of zinc in our diets will delay growth of our bodies and can kill. Hydrogen gas (H) is element #1 on the periodic table. Hydrogen was discovered in … Continue reading "How to Get Hydrogen from Zinc" |
Hydrogen Bromide
WARNING!! THIS EXPERIMENT IS PARTICULARLY DANGEROUS!! (No kidding.) This experiment is for advanced students. We've created a video that shows you how to safely do this experiment, although if you're nervous about doing this one, just watch the video and skip the actual experiment. Bromine is a particularly nasty chemical, so be sure to very … Continue reading "Hydrogen Bromide" |
Hydrogen Chlorine Gas
WARNING!! THIS EXPERIMENT IS PARTICULARLY DANGEROUS!! (No kidding.) This experiment is for advanced students. We’ve created a video that shows you how to safely do this experiment, although if you’re nervous about doing this one, just watch the video and skip the actual experiment. The gas you generate with this experiment is lethal in large … Continue reading "Hydrogen Chlorine Gas" |
Hydrogen Peroxide
This experiment is for advanced students. In industry, hydrogen peroxide is used in paper making to bleach the pulp before they form it into paper. Biologists, when preparing bones for display, use peroxide to whiten the bones. At home, 3% peroxide combined with ammonium hydroxide is used to give dark-haired people their desired blonde moment. … Continue reading "Hydrogen Peroxide" |