Now you understand how scuffing along a carpet in socks builds up electrons on the body, and how this negative electric charge affects other things (like your cat) when you reach a finger out to touch them. You also know how opposite charges attract and like charges repel, and the difference between balanced charges and unbalanced charges.
We’re going to dive into studying force fields. You may wonder what force fields have to do with a serious examination of physics like the one in this lesson. You probably consider force fields to be something you might hear about in a science fiction scene such as…
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Overall, Maxwell’s four equations describe the fundamentals of electricity and magnetism. However, one look at these mathematical equations can make a high school student run screaming from the room, so we’re not going to dive into the sophisticated mathematics of the equations themselves, but rather what they really tell us about the relationships between the electric and magnetic fields.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
A field changes the nature of the space surround the thing producing the field. A magnet produces a magnetic field which changes the nature of the space around it so that other magnets and magnetic objects are now influenced by it. Some magnetic fields (and other fields) are stronger than others, and now we’re going to learn how to measure the field strength of electric fields.
The electric field is a vector (it has magnitude and direction), and this is how you do it:
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Michael Faraday was the first to come up with the idea about electric fields. He thought of the space around a charged object as being filled with lines of force. He was trying to figure out a pattern that represented what the electric field looked like by imagining the electric field as a bubble around a charged object and how it would interact with another object that enters into that bubble. This is a little different than imagining a charge interacting with a charge. There’s a field interaction between the two charges. Every charge creates a bubble around it that in turn, affects the space within that bubble.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Have you wrapped your mind around static electricity yet? You should understand by now how scuffing along a carpet in socks builds up electrons, which eventually jump off in a flurry known as a spark. And you also probably know a bit about magnets and how magnets have north and south poles AND a magnetic field (more on this later). Did you also know that electrical charges have an electrical field, just like magnets do?
It’s easy to visualize a magnetic field, because you’ve seen the iron filings line up from pole to pole. But did you know that you can do a similar experiment with electric fields?
Here’s what you need:
- dried dill (spice)
- vegetable or mineral oil
- 2 alligator wires
- static electricity source (watch video first!)
Click here to go to next lesson on Weird Shapes and Field Lines.

Michael Faraday also discovered how you can have an electric field inside a charged conductor. Image you have a room within a room, and the inner room is made completely of metal. You can sit in the inner room with a static charge detector (like an electroscope), and when you charge the surfaces of both rooms, you’ll see sparks flying between the two rooms, but it’s peacefully (electrically speaking) quiet in the inner room. No charge is detected inside the inner room with your electroscope. You can have a bolt of lightning strike the inner room, but it still doesn’t register a charge inside the inner room. Why is that?
The inner room I’ve just described is called a “Faraday Cage”, and it’s often seen at science and magic shows because it absolutely defies common sense, until you really think about it. The inner room is shielding you from electric fields. Any closed conducting surface can be a Faraday cage. By closed, I mean electrically speaking. The cage can be a cage made of bars or chicken wire, but it’s still got to be electrically closed. During the experiment, you can even run your hands on the inside of the room and still not get a shock from the sparks flying around between the rooms!
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
You’re already familiar with two different kinds of potential energy: elastic (like the energy stored in a rubber band) and gravitational (the energy stored in height). Now let’s take a look at electrical potential energy stored in an electric field:
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
If you have a Fun Fly Stick, then pull it out and watch the video below. If not, don’t worry – you can do most of these experiments with a charged balloon (one that you’ve rubbed on your hair). Let’ play with a more static electricity experiments, including making things move, roll, spin, chime, light up, wiggle and more using static electricity!
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Alien Detector.
 This simple FET circuit is really an electronic version of the electroscope. This “Alien Detector” is a super-sensitive static charge detector made from a few electronics parts. I originally made a few of these and placed them in soap boxes and nailed the lids shut and asked kids how they worked. (I did place a on/off switch poking through the box along with the LED so they would have ‘some’ control over the experiment.)
This simple FET circuit is really an electronic version of the electroscope. This “Alien Detector” is a super-sensitive static charge detector made from a few electronics parts. I originally made a few of these and placed them in soap boxes and nailed the lids shut and asked kids how they worked. (I did place a on/off switch poking through the box along with the LED so they would have ‘some’ control over the experiment.)
This detector is so sensitive that you can go around your house and find pockets of static charge… even from your own footprints! This is an advanced project for advanced students.
You will need to get:
- 9V battery clip (and a 9V battery)
- MPF 102 (buy 2 – one for back up)
- LED (any regular LED works fine)
Click here to go to next lesson on Lightning.
What causes lightning, and how can we protect ourselves from strikes? In many textbooks, you’ll read about how clouds become electrically charged through friction in the moist air, but the truth is, scientists still don’t fully understand how and why lightning happens the way it does. But here’s what we do know: lightning happens when the positive and negative charges in a cloud become polarized. That is, the (extra) positive charges move to the top of the cloud and the (extra) negative charges move to the bottom of the cloud, usually by friction of the water vapor molecules in the cloud.
As the water molecules rise, electrons are stripped off and add to the charge of the cloud. The cloud can become ever more polarized if the rising water vapor freezes. The frozen particles clump together and take on a negative charge inside, positive charge on the outside, which rips the clumps apart to further polarize the cloud. The more polarized the cloud is, the more its electric field affects the space around it. The electrons on the surface of the Earth underneath the cloud are repelled by the bottom of the cloud, which creates a positive charge on the surface under the cloud. Trees. houses, cars, and people take on a positive charge as the cloud passes by. Now we’re set up for a lightning strike.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
The way charges attract or repel each other can be described as a force. A charge can exert a push or pull on another charge depending on if the charges are positive or negative. How much force they exert can be figured out using Coulomb’s Law of Electric Force, which is:
![]()
where C = 8.99 x 109 Nm2/C2
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
You can’t do an experiment on the planet without gravity playing some part of it (albeit sometimes so small you can ignore gravitational effects) since we’re in the Earth’s gravitational field. The electrical forces will add another force vector to our FBD that can be used when we look at how objects move in reaction to the forces.
Let’s take a look at how this works:
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Wasn’t that incredible how much force was present just between the two? After I figured that out, I wanted to know how much “push” was present between two protons in the nucleus. If you think about it, there’s really no reason for the protons to stick together inside the nucleus because they are all positively charged. Let’s take a look at the iron atom as we figure this out…
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Triboelectric series.
The Triboelectric Effect is a type of electrification that happens when you rub two different materials together and then separate them. Often, one will take on a positive charge and the other a negative. But how do you know which is going to be which?
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Electrostatic Motors.
You can use the idea that like charges repel (like two electrons) and opposites attract to move stuff around, stick to walls, float, spin, and roll. Make sure you do this experiment first.
I’ve got two different videos that use positive and negative charges to make things rotate, the first of which is more of a demonstration (unless you happen to have a 50,000 Volt electrostatic generator on hand), and the second is a homemade version on a smaller scale.
Did you know that you can make a motor turn using static electricity? Here’s how:
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Coulomb’s Law.
Induction is another way to create a charge in an object. You can charge an object by induction without even touching it. I’ve got a couple of really neat experiments that will show you how this works, but here’s the basic idea: when you have two metal objects, like two soda cans, standing upright on a foam slab and just touching each other (so they are insulated from the table but in contact with each other), you can bring a charged balloon close to one of them and see a really interesting effect: the can closest to the charged balloon (which has a negative charge) will take on a positive charge, and the soda can furthest from the balloon will take on a negative charge. And when you separate the two cans, the charges on each will be evenly distributed over the surface of each can and remain polarized (the further can keeps its negative charge and the closer can keeps its positive charge). That’s charging by induction!
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
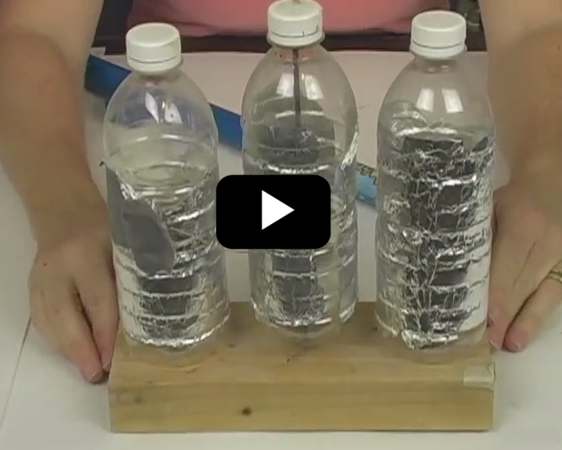
When high energy radiation strikes the Earth from space, it’s called cosmic rays. To be accurate, a cosmic ray is not like a ray of sunshine, but rather is a super-fast particle slinging through space. Think of throwing a grain of sand at a 100 mph… and that’s what we call a ‘cosmic ray’. Build your own electroscope with this video!
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Jupiter not only has the biggest lightning bolts we’ve ever detected, it also shocks its moons with a charge of 3 million amps every time they pass through certain hotspots. Some of these bolts are cause by the friction of fast-moving clouds. Today you get to make your own sparks and simulate Jupiter’s turbulent storms.
Electrons are too small for us to see with our eyes, but there are other ways to detect something’s going on. The proton has a positive charge, and the electron has a negative charge. Like charges repel and opposite charges attract.
Materials
- Foam plate
- Foam cup
- Wool cloth or sweater
- Plastic baggie
- Aluminum pie pan
- Aluminum foil
- Film canister or M&M container
- Nail (needs to be a little longer than the film canister)
- Hot glue gun or tape
- Water
Click here to go to next lesson on Easy Photoelectric Effect Experiment
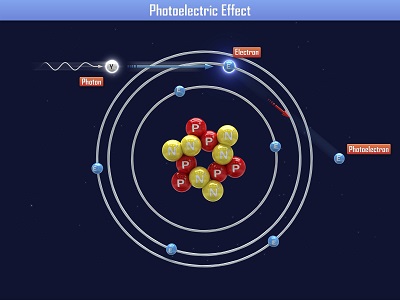 Einstein received a Nobel Prize for figuring out what happens when you shine blue light on a sheet of metal. When he aimed a blue light on a metal plate, electrons shot off the surface. (Metals have electrons which are free to move around, which is why metals are electrically conductive. More on this in Unit 10).
Einstein received a Nobel Prize for figuring out what happens when you shine blue light on a sheet of metal. When he aimed a blue light on a metal plate, electrons shot off the surface. (Metals have electrons which are free to move around, which is why metals are electrically conductive. More on this in Unit 10).
When Einstein aimed a red light at the metal sheet, nothing happened. Even when he cranked the intensity (brightness) of the red light, still nothing happened. So it was the energy of the light (wavelength), not the number of photons (intensity) that made the electrons eject from the plate. This is called the ‘photoelectric effect’. Can you imagine what happens if we aim a UV light (which has even more energy than blue light) at the plate?
This photoelectric effect is used by all sorts of things today, including solar cells, electronic components, older types of television screens, video camera detectors, and night-vision goggles.
This photoelectric effect also causes the outer shell of orbiting spacecraft to develop an electric charge, which can wreck havoc on its internal computer systems.
A surprising find was back in the 1960s, when scientists discovered that moon dust levitated through the photoelectric effect. Sunlight hit the lunar dust, which became (slightly) electrically charged, and the dust would then lift up off the surface in thin, thread-like fountains of particles up ¾ of a mile high.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Charging by Induction and Conduction.
Ygou can also charge objects by conduction. You’ve actually already done with without really thinking about it. The foil on the wire coat hanger in the electroscope was being charged by conduction. When you touch a charged balloon to the foil ball on the electroscope, that’s a charge by conduction. If you were to get the charged balloon really close but not touching the foil ball, that would be charging by induction. (See the difference?) Charging by conduction just means that you need to touch the electrically neutral object to the one that is charged to transfer the charge. It’s charge by contact.
With charge by induction, it’s the forces due to likes repelling and opposites attracting that cause the charge in objects. With conduction, it’s the actual movement of electrons to the object that make the charge in the object. This is obvious if you think about touching two soda cans together, since they are both made out of a material that allows electrons to move about freely within the material (on the surface of the object). But what about two insulators, like two foam plates? What happens then?
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
This experiment is just for advanced students. If you guessed that this has to do with electricity and chemistry, you’re right! But you might wonder how they work together. Back in 1800, William Nicholson and Johann Ritter were the first ones to split water into hydrogen and oxygen using electrolysis. (Soon afterward, Ritter went on to figure out electroplating.) They added energy in the form of an electric current into a cup of water and captured the bubbles forming into two separate cups, one for hydrogen and other for oxygen.
This experiment is not an easy one, so feel free to skip it if you need to. You don’t need to do this to get the concepts of this lesson but it’s such a neat and classical experiment (my students love it) so you can give it a try if you want to. The reason I like this is because what you are really doing in this experiment is ripping molecules apart and then later crashing them back together.
Have fun and please follow the directions carefully. This could be dangerous if you’re not careful. The image shown here is using graphite from two pencils sharpened on both ends, but the instructions below use wire. Feel free to try both to see which types of electrodes provide the best results.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Molecules and Atoms.
Let’s try another way to look at this. You’re playing miniature golf and you come to the old wind mill hole. Your friend takes a shot and since the blades of the windmill are going nice and slow he gets the ball right through. Now it’s your turn. Suddenly you hear a zap and a pow and sparks go flying. Something has gone wrong with the wind mill and it starts spinning at amazing speeds. You decide to give it a try and hit the ball towards the wind mill.
Well since it is spinning out of control, those blades now form almost a solid disk so that there is no way your ball can get through the wind mill. Electrons do the same thing. They move so fast that even though there may not be many of them, they form a shell that can’t be penetrated. (To be clear, particles that are smaller than an atom can go through the shells and pop out the other side.)
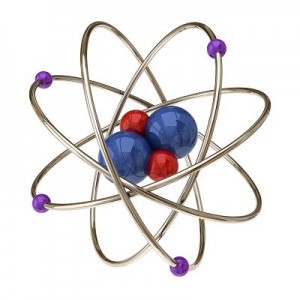 Let’s go a little further with this shell thing. An atom can have as few as one and as many as seven shells. Imagine our balloon again. Now there can be a balloon inside of a balloon inside a balloon and so on. Up to seven balloons! Each balloon, whoops, I mean shell, can have only so many electrons in it. This simple equation 2n2 tells you how many electrons can be in each shell. The n stands for the number of the shell.
Let’s go a little further with this shell thing. An atom can have as few as one and as many as seven shells. Imagine our balloon again. Now there can be a balloon inside of a balloon inside a balloon and so on. Up to seven balloons! Each balloon, whoops, I mean shell, can have only so many electrons in it. This simple equation 2n2 tells you how many electrons can be in each shell. The n stands for the number of the shell.
The first shell can have up to 2 x 1(first shell)2 or 2 electrons. The second shell can have up to 2 x 2(second shell)2 or 8 electrons. The third shell can have up to 2 x 32 or 18 electrons. The fourth shell can have up to 2 x 42 or 32 electrons. All the way up to the seventh shell which can have 2 x 72 or 98 electrons!
One last thing about shells, the shells have to be full before the electrons will go to the next shell. A helium atom will have two electrons. Both of them will be in the first shell. A Lithium atom will have three electrons. Two will be in the first shell and one (since the first shell is filled) will be in the second shell.
Electrons provide the size and stability of the atom and, as such, the mass and the structure of all matter. Electrons are also the key to all electromagnetic energy. But wait, that’s not all! It is the number of electrons in an atom that determines if and how atoms come together to form molecules. Electrons determine how and what matter will be.
Atoms like to feel satisfied and they feel satisfied if they are “full”. An atom is “full” if its outer electron shell has as many electrons as it can hold or if there are eight or a multiple of eight (16, 24 etc.) electrons in the outer shell. This is called the octet rule and works most of the time, but is not perfect.
If an atom is not full, it is not satisfied. An unsatisfied atom needs to do something with its electrons to be happy. Luckily atoms are very friendly and love to share. Most atoms are not satisfied as individuals. The oxygen atom has six electrons in its outer shell. It needs eight electrons to be satisfied.
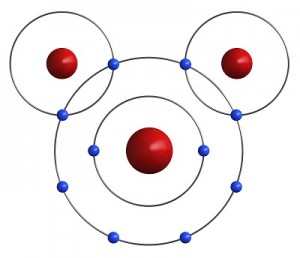 Luckily, two Hydrogen atoms happen by. Each one of them has only one electron in its outer shell and needs one more to be satisfied. If both Hydrogens share their one electron with the Oxygen, the oxygen has eight electrons and is satisfied. Also, if the Oxygen shares an electron with each Hydrogen, then both Hydrogens are satisfied as well. Just like your mother told you, it’s nice to share. It is this sharing of electrons that makes atoms come together to form molecules.
Luckily, two Hydrogen atoms happen by. Each one of them has only one electron in its outer shell and needs one more to be satisfied. If both Hydrogens share their one electron with the Oxygen, the oxygen has eight electrons and is satisfied. Also, if the Oxygen shares an electron with each Hydrogen, then both Hydrogens are satisfied as well. Just like your mother told you, it’s nice to share. It is this sharing of electrons that makes atoms come together to form molecules.
Click here to go to next lesson on Electrostatic Charge.
[/am4show]
To summarize, protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom, and tightly bound together. The proton has a positive charge while the neutron has no charge, and both of them are much larger than the electron. The tiny electron is outside the nucleus and weakly bound to the atom and carries a negative a charge.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Let’s go back to rubbing a balloon on your head. When you do this and bring it close to objects like a thin stream of water trickling out of the faucet, or small its of paper, or bubbles in the air, or even a ping pong ball on the table, did you notice now you can influence things? You can make water flick and spray, paper jump up and down, and bubbles and ping pong balls will follow your every move. But why is that?
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
An electrical circuit is like a NASCAR raceway. The electrons (racecars) zip around the race loop (wire circuit) superfast to make stuff happen. Although you can’t see the electrons zipping around the circuit, you can see the effects: lighting up LEDs, sounding buzzers, clicking relays, etc.
There are many different electrical components that make the electrons react in different ways, such as resistors (limit current), capacitors (collect a charge), transistors (gate for electrons), relays (electricity itself activates a switch), diodes (one-way street for electrons), solenoids (electrical magnet), switches (stoplight for electrons), and more. We’re going to use a combination diode-light-bulb (LED), buzzers, and motors in our circuits right now.
A CIRCUIT looks like a CIRCLE. When you connect the batteries to the LED with wire and make a circle, the LED lights up. If you break open the circle, electricity (current) doesn’t flow and the LED turns dark.
LED stands for “Light Emitting Diode”. Diodes are one-way streets for electricity – they allow electrons to flow one way but not the other.
Remember when you scuffed along the carpet? You gathered up an electric charge in your body. That charge was static until you zapped someone else. The movement of electric charge is called electric current, and is measured in amperes (A). When electric current passes through a material, it does it by electrical conduction. There are different kinds of conduction, such as metallic conduction, where electrons flow through a conductor (like metal) and electrolysis, where charged atoms (called ions) flow through liquids.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Why does metal conduct electricity?
 Make yourself a grab bag of fun things to test: copper pieces (nails or pipe pieces), zinc washers, pipe cleaners, Mylar, aluminum foil, pennies, nickels, keys, film canisters, paper clips, load stones (magnetic rock), other rocks, and just about anything else in the back of your desk drawer.
Make yourself a grab bag of fun things to test: copper pieces (nails or pipe pieces), zinc washers, pipe cleaners, Mylar, aluminum foil, pennies, nickels, keys, film canisters, paper clips, load stones (magnetic rock), other rocks, and just about anything else in the back of your desk drawer.
Certain materials conduct electricity better than others. Silver, for example, is one of the best electrical conductors on the planet, followed closely by copper and gold. Most scientists use gold contacts because, unlike silver and copper, gold does not tarnish (oxidize) as easily. Gold is a soft metal and wears away much more easily than others, but since most circuits are built for the short term (less than 50 years of use), the loss of material is unnoticeable.
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Liquid Conductors.
When an atom (like hydrogen) or molecule (like water) loses an electron (negative charge), it becomes an ion and takes on a positive charge. When an atom (or molecule) gains an electron, it becomes a negative ion. An electrolyte is any substance (like salt) that becomes a conductor of electricity when dissolved in a solvent (like water).
This type of conductor is called an ‘ionic conductor’ because once the salt is in the water, it helps along the flow of electrons from one clip lead terminal to the other so that there is a continuous flow of electricity.
This experiment is an extension of the Conductivity Tester experiment, only in this case we’re using water as a holder for different substances, like sugar and salt. You can use orange juice, lemon juice, vinegar, baking powder, baking soda, spices, cornstarch, flour, oil, soap, shampoo, and anything else you have around. Don’t forget to test out plain water for your ‘control’ in the experiment!
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.
Click here to go to next lesson on Superconductors.
When I was in 10th grade, my teammate and I designed what we thought was pretty clever: a superconductor roller coaster, which we imagined would float effortlessly above its magnetic track. Of course, our roller coaster was only designed on paper, because yttrium barium copper oxide ceramics had only just been discovered by top scientists.
Did you notice how it was smoking in the video? That’s because it was so cold! The usual problem with superconductors is that they need to be incredibly cold in order to exhibit superconductive properties. Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBa2Cu3O7) was the first compound that used liquid nitrogen for cooling, making superconductors a lot less expensive to work with – you no longer needed a cryogenic lab in order to levitate objects above a magnet.
Recently, scientists have found a way to make an amazing superconductor by taking a single crystal sapphire wafer and coating it with a thin (~1µm thick) ceramic material (yttrium barium copper oxide). Normally, the ceramic layer has no interesting magnetic or electrical properties, but that’s when you’re looking at it at room temperature. If you cool this material below -185ºC (-301ºF), it turns out that the ceramic material becomes a superconductor, meaning that it conducts electricity without resistance, with no energy loss. Zero. That’s what makes it a ‘superconductor’.
 To further understand superconductivity, it’s helpful to understand what normally happens to electricity as it flows through a wire. As you may know, energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be changed from one form to another.
To further understand superconductivity, it’s helpful to understand what normally happens to electricity as it flows through a wire. As you may know, energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be changed from one form to another.
In the case of wires, some of the electrical energy is changed to heat energy. If you’ve ever touched a wire that had been in use for a while, and discovered it was hot, you’ve experienced this. The heat energy is a waste. It simply means that less electricity gets to its final destination.
This is why superconductivity is so cool (no pun intended.) By cooling things down to temperatures near absolute zero, which is as low as temperatures can get, you can create a phenomenon where electricity flows without having any of it converted to heat.
Why do superconductors float above magnets?
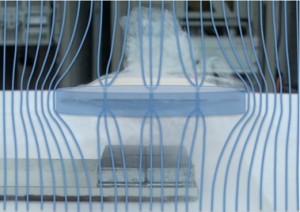 Scientists also figured out that superconductors and magnetic field really do not like each other. The Meissner effect happens when a superconductor expels all its magnetic fields from inside.
Scientists also figured out that superconductors and magnetic field really do not like each other. The Meissner effect happens when a superconductor expels all its magnetic fields from inside.
However, if you make your superconductor thin enough, you can get the magnetic field to penetrate in discrete quantities (this is real quantum physics now) called flux tubes (the blue lines that go through the disc).
Inside each of the magnetic flux tubes, the superconductivity is destroyed, but the superconductor tries to keep the magnetic tubes pinned in weak areas and any movement of the superconductor itself (like if you pushed it) causes the flux tubes to move, and this is what traps (or locks) the superconductor in midair.
If you’d like to experiment with superconductors yourself, check out this information.
Click here to go to next lesson on The difference between polarizing and charging.
Have you ever had a bad hair day? Did you happen to notice if the air was drier or wetter weather on those days? Usually folks have bad hair days when the air is drier, which is when static charge can build up more easily. Some folks notice every time they touch a doorknob, slide down a plastic slide, or scuff along the carpet in socks that they get zapped. Since there’s less water vapor in the air on drier days, there’s more of a chance for static charge to build up. The water molecule dissipates the static charge, and the more wet the air is (humid), the less static build up there is. Static electricity experiments are really hard to do on humid days, especially if it’s raining outside!
Please login or register to read the rest of this content.


